Computer Science
Welcome to Computing
You are living in the digital age, in which computers are integral to nearly every aspect of modern life. Being a confident user and creator of digital content is vital for almost all future career paths. We therefore really mean it when we say, “computing is for everyone!”.
We offer a broad curriculum, including programming, graphic design, web development and core digital literacy skills. This is designed to be highly relevant, challenging and rewarding. Bottom-line, we aim to prepare our pupils for careers in a huge range of fields, many of which may not even exist yet!
All lessons, from Year 7 to 13, are taught by specialist computing teachers. This level of technical expertise, combined with our well-structured and resourced curriculum, allows us to consistently achieve excellent outcomes throughout all key stages.
More widely, we run a range of extra-curricular activities including our highly successful Robotics Club, who in 2023 were crowned regional champions! We also have strong links with local industry and regularly have pupils undertaking work experience programmes in computing related companies.
Curriculum Intent
The computing department’s curriculum aims to provide accessible, relevant and career focused learning across all key stages. Computing is a fast-changing subject and we try to reflect this in our curriculum. As such we regularly review not only what we teach, but also how it is delivered, in order to ensure it is as modern, relevant and up to date as possible.
In computing lessons, pupils will tackle complex topics including programming and graphic design using professional level software. Support and scaffolding alongside stretch and challenge activities is at the heart of all our lessons though. In short, we pride ourselves on making computing accessible to all pupils.
Through computing lessons, pupils will learn a wide range of specialised technical skills. Beyond this though, we also embed wider digital literacy skills into lessons; skills that are vital for success no matter what career path pupils choose to follow. This makes computing a highly relevant subject for all pupils.
Computing Learning journey
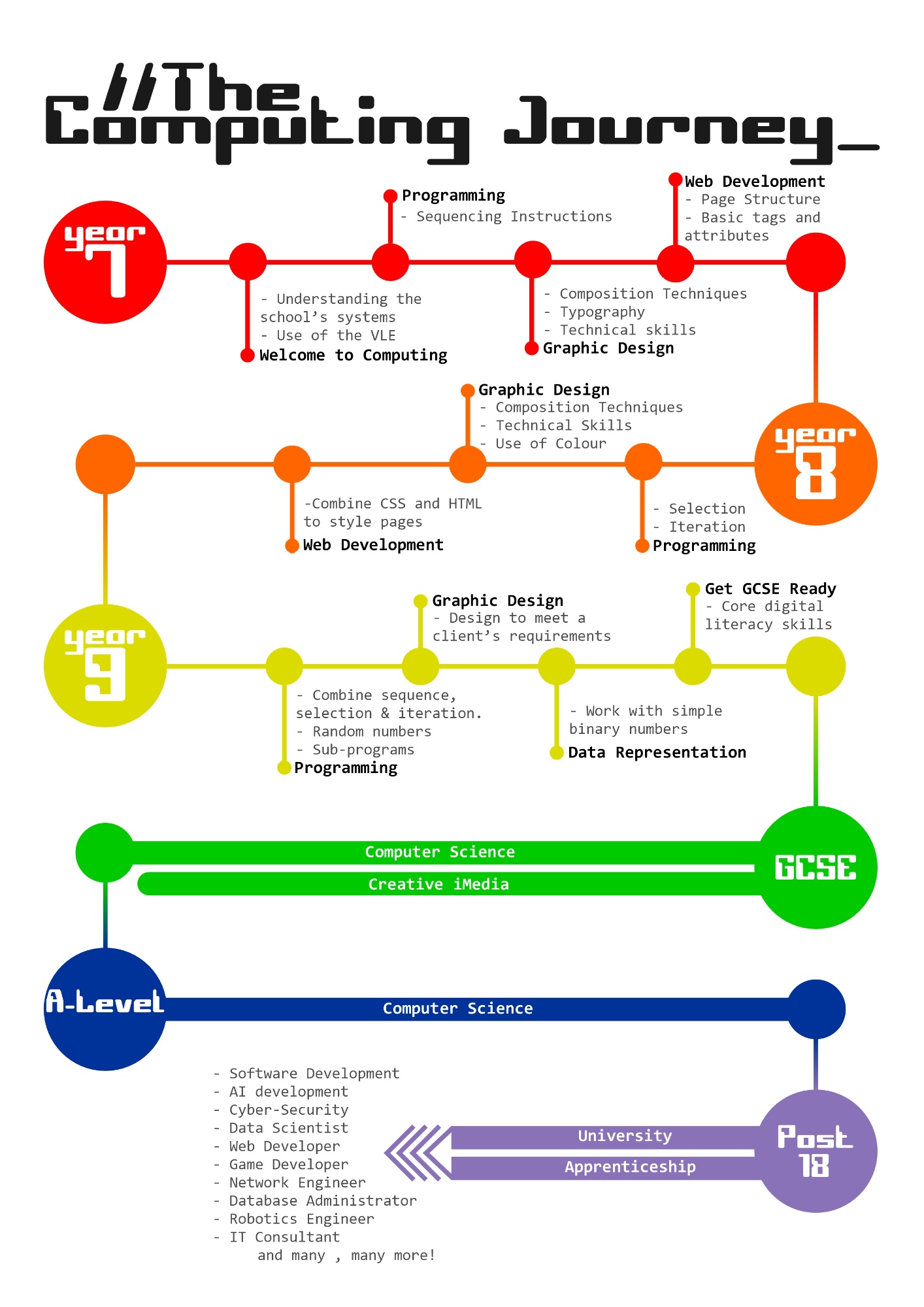
Key Stage 3
Our KS3 curriculum is designed not only to be a perfect springboard into GCSE and A-Level, but to also arm pupils with relevant digital skills to help them in any path they may follow. We employ a spiral style model, in which pupils will revisit similar topics throughout the three years. Thus allowing them to re-embed previous knowledge and then build upon it. We find this a highly successful approach to building pupils’ digital confidence
|
Key: |
Computer Science |
Creative Media |
Web Development |
Digital Skills |
|
|
Year 7 |
Year 8 |
Year 9 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Term 1 |
|||
|
Term 2 |
|||
|
Term 3 |
|||
Key Stage 4
Once pupils enter KS4, the broad subject of Computing splits into two discrete options: Computer Science and Creative iMedia.
Computer Science (OCR)
Our GCSE Computer Science course is perfect for pupils looking to follow any STEM related career path. From a practical point of view, pupils will develop the problem solving and programming skills required for so many modern careers! It isn’t all about programming though, the course also includes learning about the inner workings of computer systems and debating ethical concerns, such as the growing use of AI.
Creative iMedia (OCR)
Our Creative iMedia course is ideal for any pupil considering a career in the creative industry. This is a highly hands-on course, in which pupils will learn the fundamentals of graphic design and animation. The course is 60% coursework, which really gives pupils the opportunity to express and explore their creativity.
|
|
Computer Science |
Creative iMedia |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Year 10 |
Year 11 |
Year 10 |
Year 11 |
|
Sep |
&
|
|||
|
Oct |
||||
|
Nov |
||||
|
Dec |
||||
|
Jan |
||||
|
Feb |
||||
|
Mar |
||||
|
Apr |
||||
|
May |
Revision |
|||
|
Jun |
|
|
||
|
Jul |
Revision |
|
|
|
Key Stage 5
A-Level Computer Science is an ideal subject for pupils wishing to follow careers in areas such as software development, cyber-security and networking. The skills learned are highly transferable though and the subject supports pupils going into any STEM related career as well. The course picks up from GCSE Computer Science, but as you might expect, the depth to which we explore topics is far deeper. The course also includes a substantial practical programming project, which accounts for 20% of the overall grade. The focus of this project is down to the pupils, and it represents a chance for them to show off what they have learnt throughout the course.
|
|
A-Level Computer Science |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Year 12 |
Year 13 |
|||
|
Sep |
|||||
|
Oct |
|||||
|
Nov |
|||||
|
Dec |
|||||
|
Jan |
|||||
|
Feb |
|||||
|
Mar |
Revision |
||||
|
Apr |
|||||
|
May |
|
||||
|
Jun |
Revision |
|
|||
|
Jul |
|
||||
Future Possibilities:
Programmer, Data Analyst, Information Systems Manager, IT Consultant, Web Designer, Graphic Designer, Games Designer.
